Framework框架和调度流程
由于生产环境中Kubernetes系统的复杂性越来越高,原生default- scheduler无法满足复杂的调度需求,为了避免代码过于庞大和复杂,Kubernetes通过扩展插件Scheduler Extender和多调度器Multiple Schedulers的方式来增强调度器的可扩展性。在1.21版本GA了Scheduler Framework,调度框架解耦了核心流程与插件、通过profile配置支持插件配置和多调度器。
参考官方文档调度器配置,我们可以创建一个配置文件,包含调度过程中所需要的插件列表以及调度器实例。
// 扩展插件
apiVersion: kubescheduler.config.k8s.io/v1
kind: KubeSchedulerConfiguration
profiles:
- plugins:
score:
disabled:
- name: PodTopologySpread
enabled:
- name: MyCustomPluginA
weight: 2
- name: MyCustomPluginB
weight: 1
// 多调度器
apiVersion: kubescheduler.config.k8s.io/v1
kind: KubeSchedulerConfiguration
profiles:
- schedulerName: default-scheduler
- schedulerName: no-scoring-scheduler
plugins:
preScore:
disabled:
- name: '*'
score:
disabled:
- name: '*'
1. 配置阶段
回顾调度器配置在创建过程中的变化,在整个过程中的第一件事就是生成并补全配置信息,也就是完善一个Options结构体,整体流程如下,只保留最重要的代码部分以及和Framework相关的结构。
首先在程序入口NewSchedulerCommand处会创建一个options.Options对象,并在后续过程中一直被使用和更改。
// cmd路径下的调度器创建入口
func NewSchedulerCommand(registryOptions ...Option) *cobra.Command {
......
// 新建对象
opts := options.NewOptions()
cmd := &cobra.Command{
......
// 把opt传入runCommand
RunE: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) error {
return runCommand(cmd, opts, registryOptions...)
}
......
}
实际创建逻辑runCommand中,Options对象被用于生成CompletedConfig配置信息和Scheduler实例。
func runCommand(cmd *cobra.Command, opts *options.Options, registryOptions ...Option) error {
......
cc, sched, err := Setup(ctx, opts, registryOptions...)
return Run(ctx, cc, sched)
}
在Setup以前,Options对象中的配置主要是开关类型,在这个流程中被赋值,然后根据Options对象创建Config类型并传入到调度器实例的创建参数中。
func Setup(ctx context.Context, opts *options.Options, outOfTreeRegistryOptions ...Option) (*schedulerserverconfig.CompletedConfig, *scheduler.Scheduler, error) {
// 从这里开始给Options对象注入ComponentConfig字段
if cfg, err := latest.Default(); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
} else {
opts.ComponentConfig = cfg
}
......
// 根据Options对象创建Config类型 内部的ApplyTo方法merge了文件配置和默认配置
c, err := opts.Config(ctx)
// 封装成CompletedConfig类型
cc := c.Complete()
......
sched, err := scheduler.New(ctx,
cc.Client,
cc.InformerFactory,
cc.DynInformerFactory,
recorderFactory,
// 在创建调度器实例时传入CompletedConfig
scheduler.WithComponentConfigVersion(cc.ComponentConfig.TypeMeta.APIVersion),
scheduler.WithKubeConfig(cc.KubeConfig),
scheduler.WithProfiles(cc.ComponentConfig.Profiles...),
scheduler.WithPercentageOfNodesToScore(cc.ComponentConfig.PercentageOfNodesToScore),
......
)
}
New()函数中真正创建了Framework对象,也就是profile.Map类型的集合,并将其赋值给调度器实例。
var defaultSchedulerOptions = schedulerOptions{
percentageOfNodesToScore: schedulerapi.DefaultPercentageOfNodesToScore,
podInitialBackoffSeconds: int64(internalqueue.DefaultPodInitialBackoffDuration.Seconds()),
podMaxBackoffSeconds: int64(internalqueue.DefaultPodMaxBackoffDuration.Seconds()),
podMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration: internalqueue.DefaultPodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration,
parallelism: int32(parallelize.DefaultParallelism),
applyDefaultProfile: true,
}
func New(ctx context.Context,
client clientset.Interface,
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory,
dynInformerFactory dynamicinformer.DynamicSharedInformerFactory,
recorderFactory profile.RecorderFactory,
opts ...Option) (*Scheduler, error) {
......
// 初始化schedulerOptions对象
options := defaultSchedulerOptions
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(&options)
}
// New使用了WithProfiles此处为false
if options.applyDefaultProfile {
var versionedCfg configv1.KubeSchedulerConfiguration
scheme.Scheme.Default(&versionedCfg)
cfg := schedulerapi.KubeSchedulerConfiguration{}
if err := scheme.Scheme.Convert(&versionedCfg, &cfg, nil); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
options.profiles = cfg.Profiles
}
// 创建Profile的集合 类型为profile.Map
profiles, err := profile.NewMap(ctx, options.profiles, registry, recorderFactory,
frameworkruntime.WithComponentConfigVersion(options.componentConfigVersion),
frameworkruntime.WithClientSet(client),
frameworkruntime.WithKubeConfig(options.kubeConfig),
......
)
......
sched := &Scheduler{
Cache: schedulerCache,
client: client,
nodeInfoSnapshot: snapshot,
percentageOfNodesToScore: options.percentageOfNodesToScore,
Extenders: extenders,
StopEverything: stopEverything,
SchedulingQueue: podQueue,
Profiles: profiles,
logger: logger,
}
......
return sched, nil
}
NewMap()函数的实现如下,遍历KubeSchedulerProfile对象,生成Framework对象作为value,SchedulerName作为key,组成一个Map对象返回给上层。
type Map map[string]framework.Framework
func NewMap(ctx context.Context, cfgs []config.KubeSchedulerProfile, r frameworkruntime.Registry, recorderFact RecorderFactory,
opts ...frameworkruntime.Option) (Map, error) {
m := make(Map)
v := cfgValidator{m: m}
// 遍历profile
for _, cfg := range cfgs {
// KubeSchedulerProfile -> Framework
p, err := newProfile(ctx, cfg, r, recorderFact, opts...)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("creating profile for scheduler name %s: %v", cfg.SchedulerName, err)
}
if err := v.validate(cfg, p); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
m[cfg.SchedulerName] = p
}
return m, nil
}
func newProfile(ctx context.Context, cfg config.KubeSchedulerProfile, r frameworkruntime.Registry, recorderFact RecorderFactory,
opts ...frameworkruntime.Option) (framework.Framework, error) {
recorder := recorderFact(cfg.SchedulerName)
opts = append(opts, frameworkruntime.WithEventRecorder(recorder))
return frameworkruntime.NewFramework(ctx, r, &cfg, opts...)
}
NewFramework是调度框架的初始化入口,根据KubeSchedulerProfile创建Framework实例,每个Framework对象对应的就是一个调度器的业务逻辑配置。
func NewFramework(ctx context.Context, r Registry, profile *config.KubeSchedulerProfile, opts ...Option) (framework.Framework, error) {
options := defaultFrameworkOptions(ctx.Done())
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(&options)
}
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
if options.logger != nil {
logger = *options.logger
}
// 初始化frameworkImpl实例
// 各种组件通过With作为Option传递并注入
f := &frameworkImpl{
registry: r,
snapshotSharedLister: options.snapshotSharedLister,
scorePluginWeight: make(map[string]int),
waitingPods: options.waitingPods,
clientSet: options.clientSet,
kubeConfig: options.kubeConfig,
eventRecorder: options.eventRecorder,
informerFactory: options.informerFactory,
sharedDRAManager: options.sharedDRAManager,
metricsRecorder: options.metricsRecorder,
extenders: options.extenders,
PodNominator: options.podNominator,
PodActivator: options.podActivator,
parallelizer: options.parallelizer,
logger: logger,
}
if len(f.extenders) > 0 {
f.enqueueExtensions = []framework.EnqueueExtensions{&defaultEnqueueExtension{pluginName: framework.ExtenderName}}
}
if profile == nil {
return f, nil
}
f.profileName = profile.SchedulerName
f.percentageOfNodesToScore = profile.PercentageOfNodesToScore
if profile.Plugins == nil {
return f, nil
}
// 根据配置文件记录启用的插件列表(这个集合与扩展点无关 仅为了确定初始化哪些插件) Set结构天生去重
pg := f.pluginsNeeded(profile.Plugins)
pluginConfig := make(map[string]runtime.Object, len(profile.PluginConfig))
// 记录每种插件的自定义配置Args参数列表 用于下面的插件初始化
for i := range profile.PluginConfig {
name := profile.PluginConfig[i].Name
if _, ok := pluginConfig[name]; ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("repeated config for plugin %s", name)
}
pluginConfig[name] = profile.PluginConfig[i].Args
}
outputProfile := config.KubeSchedulerProfile{
SchedulerName: f.profileName,
PercentageOfNodesToScore: f.percentageOfNodesToScore,
Plugins: profile.Plugins,
PluginConfig: make([]config.PluginConfig, 0, len(pg)),
}
f.pluginsMap = make(map[string]framework.Plugin)
// 遍历Registry中注册的工厂函数
for name, factory := range r {
// 只加载使用到的插件
if !pg.Has(name) {
continue
}
// 获取插件参数
args := pluginConfig[name]
if args != nil {
outputProfile.PluginConfig = append(outputProfile.PluginConfig, config.PluginConfig{
Name: name,
Args: args,
})
}
// 调用构造函数创建插件实例
p, err := factory(ctx, args, f)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("initializing plugin %q: %w", name, err)
}
// 保存到插件集合中
f.pluginsMap[name] = p
// 设置EnqueueExtensions 用于监听入队事件 可用于任意阶段
f.fillEnqueueExtensions(p)
}
// 给扩展点配置插件链,根据指针的指向实际是填充了如[]framework.FilterPlugin的插件列表
for _, e := range f.getExtensionPoints(profile.Plugins) {
// 通过反射修改 slicePtr指向[]framework.xxxPlugin对象 所以实际是修改了frameworkImpl.xxxPlugins字段的切片内容
if err := updatePluginList(e.slicePtr, *e.plugins, f.pluginsMap); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
// 如果有多扩展点插件(可作用于12标准流程中的多个扩展点),把添加到对应的插件链中
if len(profile.Plugins.MultiPoint.Enabled) > 0 {
if err := f.expandMultiPointPlugins(logger, profile); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
// 必须有一个QueueSortPlugin
if len(f.queueSortPlugins) != 1 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("only one queue sort plugin required for profile with scheduler name %q, but got %d", profile.SchedulerName, len(f.queueSortPlugins))
}
// 必须有BindPlugin
if len(f.bindPlugins) == 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("at least one bind plugin is needed for profile with scheduler name %q", profile.SchedulerName)
}
// 设置ScorePlugin插件权重
if err := getScoreWeights(f, append(profile.Plugins.Score.Enabled, profile.Plugins.MultiPoint.Enabled...)); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 校验ScorePlugin插件权重
for _, scorePlugin := range f.scorePlugins {
if f.scorePluginWeight[scorePlugin.Name()] == 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("score plugin %q is not configured with weight", scorePlugin.Name())
}
}
// 如果调度器的启动参数中设置了捕获配置 把outputProfile写入captureProfile字段
if options.captureProfile != nil {
if len(outputProfile.PluginConfig) != 0 {
sort.Slice(outputProfile.PluginConfig, func(i, j int) bool {
return outputProfile.PluginConfig[i].Name < outputProfile.PluginConfig[j].Name
})
} else {
outputProfile.PluginConfig = nil
}
options.captureProfile(outputProfile)
}
logger.V(2).Info("the scheduler starts to work with those plugins", "Plugins", *f.ListPlugins())
// 给插件注入监控指标
f.setInstrumentedPlugins()
return f, nil
}
1.1. 配置相关的类型梳理
总结配置中的一些核心结构,最顶层的配置结构是Options,是进程级别的全局配置参数,在NewOptions()函数中解析命令行参数并初始化,如--kubeconfig和--port等,主要承载了调度器组件的启动参数。
type Options struct {
// 只关注ComponentConfig类型 在Setup阶段被赋值
ComponentConfig *kubeschedulerconfig.KubeSchedulerConfiguration
SecureServing *apiserveroptions.SecureServingOptionsWithLoopback
Authentication *apiserveroptions.DelegatingAuthenticationOptions
Authorization *apiserveroptions.DelegatingAuthorizationOptions
Metrics *metrics.Options
Logs *logs.Options
Deprecated *DeprecatedOptions
LeaderElection *componentbaseconfig.LeaderElectionConfiguration
ConfigFile string
WriteConfigTo string
Master string
ComponentGlobalsRegistry featuregate.ComponentGlobalsRegistry
Flags *cliflag.NamedFlagSets
}
在Setup阶段(更准确地说是在ApplyTo()方法)基于Options生成了Config/CompletedConfig对象,合并了配置文件以及默认配置的内容,并在后续直接使用的是CompletedConfig去创建调度器实例,其中Config类型我们不特别关注,仍关注其中的字段ComponentConfig也就是类型KubeSchedulerConfiguration。
type Config struct {
// 和Options中的ComponentConfig意义完全相同
ComponentConfig kubeschedulerconfig.KubeSchedulerConfiguration
LoopbackClientConfig *restclient.Config
Authentication apiserver.AuthenticationInfo
Authorization apiserver.AuthorizationInfo
SecureServing *apiserver.SecureServingInfo
Client clientset.Interface
KubeConfig *restclient.Config
InformerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory
DynInformerFactory dynamicinformer.DynamicSharedInformerFactory
EventBroadcaster events.EventBroadcasterAdapter
LeaderElection *leaderelection.LeaderElectionConfig
PodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration time.Duration
}
KubeSchedulerConfiguration类型的初始化也是在Setup中,字段Profiles是KubeSchedulerProfile的切片类型,所以支持多调度器配置,该结构的来源是调度器配置的静态文件,默认配置可以查找SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration()函数,此函数逻辑在pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1/register.go中的init()被调用。
type KubeSchedulerConfiguration struct {
metav1.TypeMeta
Parallelism int32
LeaderElection componentbaseconfig.LeaderElectionConfiguration
ClientConnection componentbaseconfig.ClientConnectionConfiguration
componentbaseconfig.DebuggingConfiguration
PercentageOfNodesToScore *int32
PodInitialBackoffSeconds int64
PodMaxBackoffSeconds int64
// key是调度器名称 value是Framework实例
Profiles []KubeSchedulerProfile
Extenders []Extender
DelayCacheUntilActive bool
}
KubeSchedulerProfile类型包含了各阶段PluginSet的指针和调度器名称,是在调度框架流程中具体的调度配置。
type KubeSchedulerProfile struct {
// profile名称
SchedulerName string
// 打分节点抽样比例
PercentageOfNodesToScore *int32
// 插件集合
Plugins *Plugins
// 插件配置Args
PluginConfig []PluginConfig
}
在New()函数初始化了schedulerOptions对象,是根据KubeSchedulerProfile而来的核心子集,仅包括调度器核心逻辑参数。
type schedulerOptions struct {
componentConfigVersion string
kubeConfig *restclient.Config
percentageOfNodesToScore int32
podInitialBackoffSeconds int64
podMaxBackoffSeconds int64
podMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration time.Duration
frameworkOutOfTreeRegistry frameworkruntime.Registry
// 由schedulerOptions.profiles赋值而来
profiles []schedulerapi.KubeSchedulerProfile
extenders []schedulerapi.Extender
frameworkCapturer FrameworkCapturer
parallelism int32
applyDefaultProfile bool
}
NewMap使用schedulerOptions.profiles创建Map/frameworkImpl,frameworkImpl实现了Framework接口,每个frameworkImpl就代表一份动态的运行时配置,这也是调度周期中使用到的核心配置。
type Map map[string]framework.Framework
type frameworkImpl struct {
registry Registry
snapshotSharedLister framework.SharedLister
waitingPods *waitingPodsMap
scorePluginWeight map[string]int
// 12个标准阶段的插件列表
preEnqueuePlugins []framework.PreEnqueuePlugin
// 入队事件扩展点
enqueueExtensions []framework.EnqueueExtensions
queueSortPlugins []framework.QueueSortPlugin
preFilterPlugins []framework.PreFilterPlugin
filterPlugins []framework.FilterPlugin
postFilterPlugins []framework.PostFilterPlugin
preScorePlugins []framework.PreScorePlugin
scorePlugins []framework.ScorePlugin
reservePlugins []framework.ReservePlugin
preBindPlugins []framework.PreBindPlugin
bindPlugins []framework.BindPlugin
postBindPlugins []framework.PostBindPlugin
permitPlugins []framework.PermitPlugin
pluginsMap map[string]framework.Plugin
clientSet clientset.Interface
kubeConfig *restclient.Config
eventRecorder events.EventRecorder
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory
sharedDRAManager framework.SharedDRAManager
logger klog.Logger
metricsRecorder *metrics.MetricAsyncRecorder
profileName string
percentageOfNodesToScore *int32
extenders []framework.Extender
framework.PodNominator
framework.PodActivator
parallelizer parallelize.Parallelizer
}
Framework接口定义如下,可以看出主要还是和插件相关。
type Framework interface {
Handle
// PreEnqueuePlugins returns the registered preEnqueue plugins.
PreEnqueuePlugins() []PreEnqueuePlugin
// EnqueueExtensions returns the registered Enqueue extensions.
EnqueueExtensions() []EnqueueExtensions
// QueueSortFunc returns the function to sort pods in scheduling queue
QueueSortFunc() LessFunc
// RunPreFilterPlugins runs the set of configured PreFilter plugins. It returns
// *Status and its code is set to non-success if any of the plugins returns
// anything but Success. If a non-success status is returned, then the scheduling
// cycle is aborted.
// It also returns a PreFilterResult, which may influence what or how many nodes to
// evaluate downstream.
// The third returns value contains PreFilter plugin that rejected some or all Nodes with PreFilterResult.
// But, note that it doesn't contain any plugin when a plugin rejects this Pod with non-success status,
// not with PreFilterResult.
RunPreFilterPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) (*PreFilterResult, *Status, sets.Set[string])
// RunPostFilterPlugins runs the set of configured PostFilter plugins.
// PostFilter plugins can either be informational, in which case should be configured
// to execute first and return Unschedulable status, or ones that try to change the
// cluster state to make the pod potentially schedulable in a future scheduling cycle.
RunPostFilterPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, filteredNodeStatusMap NodeToStatusReader) (*PostFilterResult, *Status)
// RunPreBindPlugins runs the set of configured PreBind plugins. It returns
// *Status and its code is set to non-success if any of the plugins returns
// anything but Success. If the Status code is "Unschedulable", it is
// considered as a scheduling check failure, otherwise, it is considered as an
// internal error. In either case the pod is not going to be bound.
RunPreBindPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// RunPostBindPlugins runs the set of configured PostBind plugins.
RunPostBindPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string)
// RunReservePluginsReserve runs the Reserve method of the set of
// configured Reserve plugins. If any of these calls returns an error, it
// does not continue running the remaining ones and returns the error. In
// such case, pod will not be scheduled.
RunReservePluginsReserve(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// RunReservePluginsUnreserve runs the Unreserve method of the set of
// configured Reserve plugins.
RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string)
// RunPermitPlugins runs the set of configured Permit plugins. If any of these
// plugins returns a status other than "Success" or "Wait", it does not continue
// running the remaining plugins and returns an error. Otherwise, if any of the
// plugins returns "Wait", then this function will create and add waiting pod
// to a map of currently waiting pods and return status with "Wait" code.
// Pod will remain waiting pod for the minimum duration returned by the Permit plugins.
RunPermitPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// WaitOnPermit will block, if the pod is a waiting pod, until the waiting pod is rejected or allowed.
WaitOnPermit(ctx context.Context, pod *v1.Pod) *Status
// RunBindPlugins runs the set of configured Bind plugins. A Bind plugin may choose
// whether or not to handle the given Pod. If a Bind plugin chooses to skip the
// binding, it should return code=5("skip") status. Otherwise, it should return "Error"
// or "Success". If none of the plugins handled binding, RunBindPlugins returns
// code=5("skip") status.
RunBindPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// HasFilterPlugins returns true if at least one Filter plugin is defined.
HasFilterPlugins() bool
// HasPostFilterPlugins returns true if at least one PostFilter plugin is defined.
HasPostFilterPlugins() bool
// HasScorePlugins returns true if at least one Score plugin is defined.
HasScorePlugins() bool
// ListPlugins returns a map of extension point name to list of configured Plugins.
ListPlugins() *config.Plugins
// ProfileName returns the profile name associated to a profile.
ProfileName() string
// PercentageOfNodesToScore returns percentageOfNodesToScore associated to a profile.
PercentageOfNodesToScore() *int32
// SetPodNominator sets the PodNominator
SetPodNominator(nominator PodNominator)
// SetPodActivator sets the PodActivator
SetPodActivator(activator PodActivator)
// Close calls Close method of each plugin.
Close() error
}
2. 调度的阶段
调度流程被标准化为了12个阶段,每个阶段都可以进行扩展,在Plugins结构体中可以看出这些阶段的顺序,对应下图,通过对调度器不断的了解,会发现它的重要性。
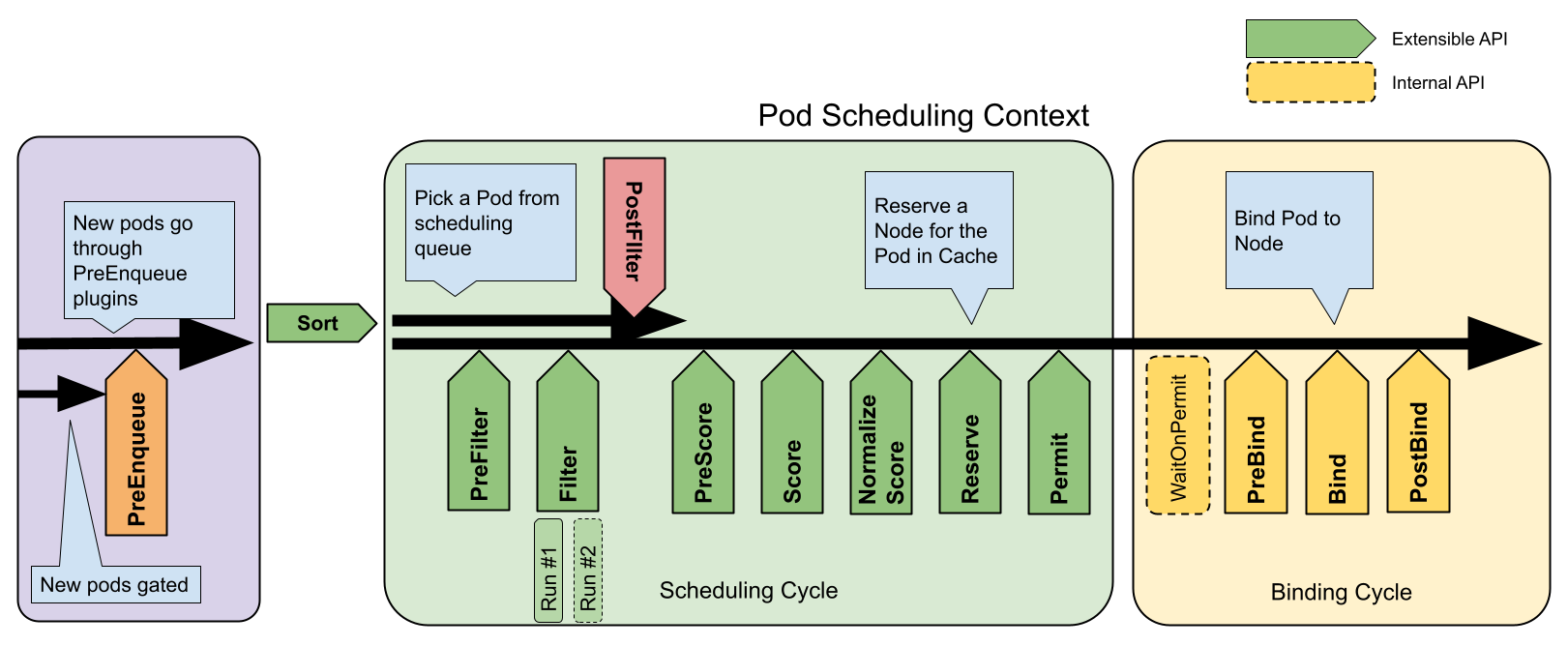
在Plugins结构体的定义中,包含了12个标准阶段的插件集合,以及一个多扩展点插件集合的字段。
type Plugins struct {
PreEnqueue PluginSet
QueueSort PluginSet
PreFilter PluginSet
Filter PluginSet
PostFilter PluginSet
PreScore PluginSet
Score PluginSet
Reserve PluginSet
Permit PluginSet
PreBind PluginSet
Bind PluginSet
PostBind PluginSet
MultiPoint PluginSet
}
已经了解了Framework的由来以及插件扩展点,所谓Framework就是一份kube-scheduler在运行时用到的配置信息,改变了最初调度算法都硬编码在流程里对于程序扩展的限制,正如目前的大多数扩展性较好的项目如PostgreSQL,都是插件化的,调度器也通过Scheduler Framework实现了这一点。
从上图中可以看出,在Pod加入调度队列以后,包含了两个Cycle,也就是说在整个调度的过程中,包含两个大的生命周期。在Scheduler创建流程与调度队列提到过实例启动的最外层逻辑是Run()方法。
// Run begins watching and scheduling. It starts scheduling and blocked until the context is done.
func (sched *Scheduler) Run(ctx context.Context) {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
// 启动调度队列
sched.SchedulingQueue.Run(logger)
// 启动调度循环
go wait.UntilWithContext(ctx, sched.ScheduleOne, 0)
// 阻塞 等待关闭信号
<-ctx.Done()
// 关闭调度队列
sched.SchedulingQueue.Close()
// 关闭调度插件
err := sched.Profiles.Close()
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "Failed to close plugins")
}
}
在本文中,我们重点关注调度的整体流程,也就是通过协程启动的sched.ScheduleOne()循环。其中的wait.UntilWithContext()函数接收三个参数,分别是上下文对象、循环执行的函数、以及循环的间隔,所以调度时就是不间断地执行sched.ScheduleOne()方法。先来简单地了解ScheduleOne()的整体实现,有关两个周期的具体实现会在后续深入说明。
func (sched *Scheduler) ScheduleOne(ctx context.Context) {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
// 从调度队列Pop出一个QueuedPodInfo对象 用于调度生命周期中
podInfo, err := sched.NextPod(logger)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "Error while retrieving next pod from scheduling queue")
return
}
// pod could be nil when schedulerQueue is closed
if podInfo == nil || podInfo.Pod == nil {
return
}
// 获取Pod对象 用于获取Pod直接相关的信息
pod := podInfo.Pod
logger = klog.LoggerWithValues(logger, "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
ctx = klog.NewContext(ctx, logger)
logger.V(4).Info("About to try and schedule pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
// 每一轮都获取配置 允许在不重启调度器的情况下动态更新策略
// 根据PodSpec的SchedulerName获取对应的Framework(可能存在多调度器配置) 如果Pod没有配置调度器则会在SetDefaults_PodSpec过程中注入默认的"default-scheduler"
fwk, err := sched.frameworkForPod(pod)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "Error occurred")
// 如果一个Pod不被调度处理 也会在Pop之后通过Done()通知ActiveQ该Pod处理完毕
sched.SchedulingQueue.Done(pod.UID)
return
}
// 如果Pod正在被删除或已经假定调度了就不处理
if sched.skipPodSchedule(ctx, fwk, pod) {
// We don't put this Pod back to the queue, but we have to cleanup the in-flight pods/events.
sched.SchedulingQueue.Done(pod.UID)
return
}
logger.V(3).Info("Attempting to schedule pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
// 记录开始调度的时间
start := time.Now()
// 初始化CycleState对象
state := framework.NewCycleState()
// 生成随机数 如果值小于10就记录插件指标
state.SetRecordPluginMetrics(rand.Intn(100) < pluginMetricsSamplePercent)
// 初始化一个空的待激活Pod集合
podsToActivate := framework.NewPodsToActivate()
// 把待激活Pod集合写入CycleState中 key为"kubernetes.io/pods-to-activate" value为podsToActivate集合
state.Write(framework.PodsToActivateKey, podsToActivate)
// 创建一个子Context用于SchedulingCycle
schedulingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
// 执行调度周期逻辑 返回结果信息、Pod信息和状态信息
scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, status := sched.schedulingCycle(schedulingCycleCtx, state, fwk, podInfo, start, podsToActivate)
// 如果调度周期返回的结果不是Success 执行调度失败处理逻辑
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.FailureHandler(schedulingCycleCtx, fwk, assumedPodInfo, status, scheduleResult.nominatingInfo, start)
return
}
// 匿名函数启动异步的绑定周期
go func() {
// 创建绑定周期上下文
bindingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
// 结束时取消上下文 避免资源泄漏
defer cancel()
// 记录绑定中的数量 开始时+1 结束时-1
metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Inc()
defer metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Dec()
// 执行绑定周期逻辑 返回绑定状态
status := sched.bindingCycle(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, start, podsToActivate)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
// 如果绑定失败 执行绑定失败处理逻辑
sched.handleBindingCycleError(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, assumedPodInfo, start, scheduleResult, status)
return
}
}()
}
通过上面的代码可以看出,在一个Pod调度的的完整生命周期中,CycleState是Pod专属上下文,负责在调度过程中传递和共享状态信息。共存在三个动作,即Pod出队、调度、异步绑定,其中Pod出队动作比较简单,经过Scheduler创建流程与调度队列中调度队列部分的学习,可以知道Pop()动作就是弹出ActiveQ的队首元素,如果队列为空会阻塞等待唤醒。调度和绑定是两个清晰的生命周期,其中调度周期的扩展点以ReservePlugins,此时默认Pod会被调度成功,提前预留资源刷新调度缓存,Pod的内部状态为Assumed。绑定周期由于包括存储、网络等资源的设置而耗时较长所以异步执行,可以理解为在完成一个Pod的节点计算选择,就立刻进入了下一个Pod的调度。